Introduction
Magnesium plays a crucial role in heart health, working tirelessly to keep the heart working at its best. However, many Americans are not getting enough magnesium in their diets, with estimates suggesting up to 75% of Americans might be magnesium deficient. This article explores the benefits of magnesium, including boosting heart health and supporting mental well-being, and provides practical tips on increasing magnesium intake through diet and supplementation. By understanding the importance of magnesium, individuals can improve their overall health and experience the magic of magnesium.
Benefits of taking magnesium at night
Taking magnesium at night can offer several benefits, particularly for sleep and overall health. Here are some key advantages:
Improved Sleep Quality
- Easier to Fall Asleep: Magnesium helps regulate neurotransmitters that calm the nervous system, making it easier to fall asleep.
- Better Sleep Quality: It can improve the overall quality of sleep by promoting deeper and more restful sleep.
- Reduced Restless Legs Syndrome: Magnesium may alleviate symptoms of restless legs syndrome, which can interfere with a good night’s sleep.
Muscle Relaxation
Magnesium helps relax muscles, which can reduce nighttime cramps and discomfort, contributing to better sleep.
Stress Reduction
Magnesium can lower cortisol levels, the stress hormone, helping you feel more relaxed and ready for sleep.
Regulation of Melatonin
Magnesium plays a role in the production of melatonin, the hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles.
Additional Health Benefits
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Magnesium can help lower blood pressure, which is beneficial for cardiovascular health.
- Blood Sugar Control: It may improve blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Migraine Prevention: Regular magnesium intake can help reduce the frequency and severity of migraines.

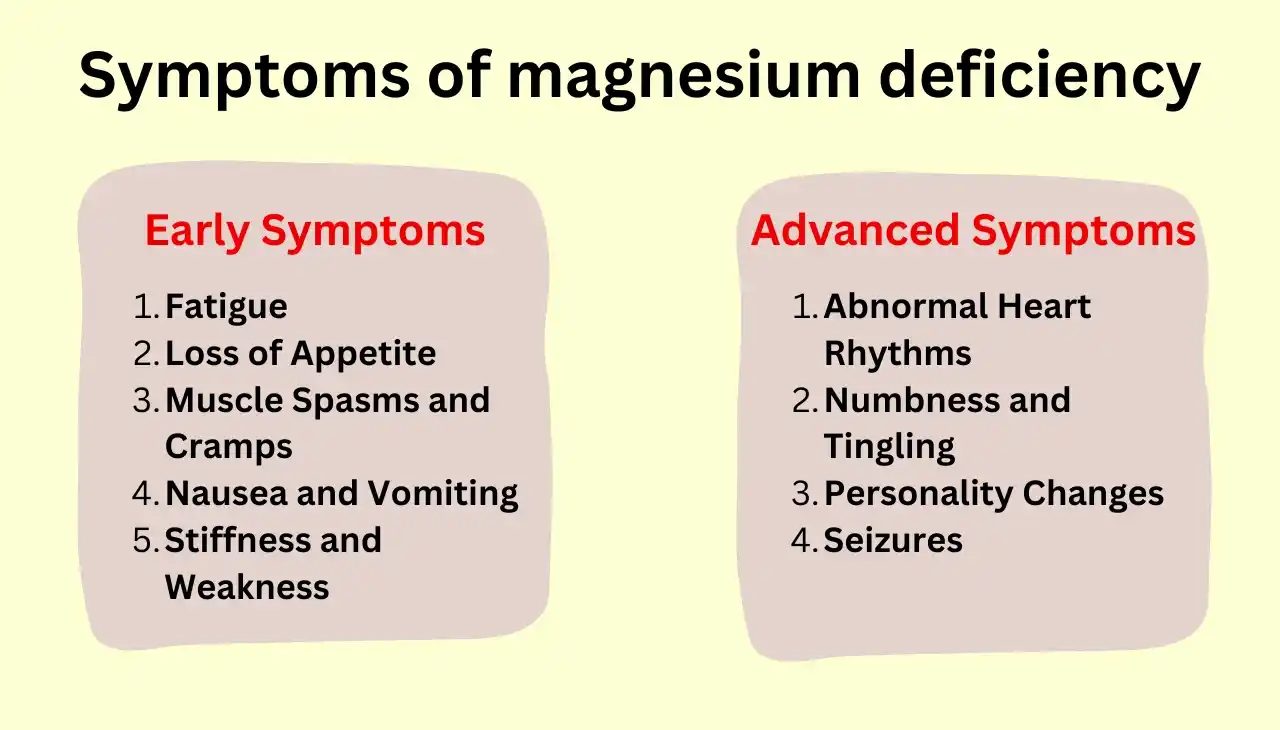
Symptoms of magnesium deficiency
Magnesium deficiency, also known as hypomagnesemia, can manifest through various symptoms, which can be both physical and mental.
Early Symptoms
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or weak.
- Loss of Appetite: Reduced desire to eat.
- Muscle Spasms and Cramps: Involuntary muscle contractions and cramps.
- Nausea and Vomiting: If you’re feeling queasy or dealing with vomiting.
- Stiffness and Weakness: Generalized muscle stiffness and weakness.
Advanced Symptoms
- Abnormal Heart Rhythms: Irregular heartbeat or palpitations.
- Numbness and Tingling: Sensations of numbness or tingling, especially in the extremities.
- Personality Changes: Mood swings, irritability, or other personality changes.
- Seizures: Remember, in extreme situations, not having enough magnesium in your body can even cause seizures.
Other Potential Symptoms
- Mental Health Issues: Increased risk of stress, depression, and anxiety.
- Osteoporosis: Fracture Risk Rises with Weak Bones
If you suspect you might have a magnesium deficiency, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider. They can run tests to confirm the deficiency and recommend appropriate treatments or dietary adjustments.
Magnesium benefits for women
Magnesium is essential for women’s health, offering a range of benefits that support various bodily functions and overall well-being. Here are some key benefits:
Hormone Regulation
- Estrogen Synthesis and Excretion: Magnesium plays a crucial role in the synthesis and excretion of estrogen, helping to maintain hormonal balance.
Bone Health
- Bone Strength and Density: Magnesium is vital for maintaining strong and healthy bones, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
Pregnancy Support
- Healthy Pregnancy: Adequate magnesium levels are important during pregnancy for both the mother’s and baby’s health.
Menstrual Health
- PMS Relief: Magnesium can help alleviate symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS), such as bloating, mood swings, and cramps.
- Stress and Anxiety Reduction: Magnesium helps regulate cortisol levels, the stress hormone, which can reduce anxiety and improve mood.
- Depression: It has been shown to help fight depression by supporting neurotransmitter function.
Metabolic Health
- Blood Sugar Control: Magnesium helps regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: It can help lower blood pressure, which is beneficial for cardiovascular health.
Physical Performance
- Exercise Performance: Magnesium supports muscle function and energy production, enhancing physical performance.
Migraine Prevention
- Migraine Relief: Regular magnesium intake can help reduce the frequency and severity of migraines.
How much magnesium per day for a women
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) of magnesium for women varies by age and physiological conditions:
- Women aged 19-30 years: 310 milligrams per day.
- Women aged 31 years and older: 320 milligrams per day.
- Pregnant women: 350-360 milligrams per day.
It’s important to note that these recommendations include magnesium from both food and supplements. If you’re considering taking a magnesium supplement, it’s a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the right dosage for your specific needs.
Magnesium rich foods
Nuts and Seeds
- Almonds: 1 ounce (28 grams) provides about 80 mg of magnesium.
- Cashews: 1 ounce (28 grams) provides about 72 mg of magnesium.
- Pumpkin Seeds: 1 ounce (28 grams) provides about 150 mg of magnesium.
- Chia Seeds: 1 ounce (28 grams) provides about 111 mg of magnesium.
Legumes
- Black Beans: 1/2 cup (86 grams) provides about 60 mg of magnesium.
- Edamame: 1/2 cup (78 grams) provides about 50 mg of magnesium.
- Lima Beans: 1/2 cup (85 grams) provides about 40 mg of magnesium.
Whole Grains
- Quinoa: 1/2 cup (92 grams) provides about 60 mg of magnesium.
- Brown Rice: 1 cup (195 grams) provides about 84 mg of magnesium.
Vegetables
- Spinach: 1 cup (180 grams) cooked provides about 157 mg of magnesium.
- Swiss Chard: 1 cup (175 grams) cooked provides about 150 mg of magnesium.
Fruits
- Avocados: 1 medium avocado provides about 58 mg of magnesium.
- Bananas: 1 medium banana provides about 32 mg of magnesium.
Dairy
- Yogurt: 1 cup (245 grams) provides about 50 mg of magnesium.
- Milk: 1 cup (244 grams) provides about 24 mg of magnesium.
Other
- Dark Chocolate: 1 ounce (28 grams) provides about 65 mg of magnesium.
Consuming a mix of these foods can help you reach your daily magnesium requirements.

Magnesium benefits for men
Magnesium offers numerous health benefits for men, supporting various bodily functions and overall well-being. Here are some key benefits:
Hormonal Health
- Testosterone Levels: Magnesium can help regulate and boost free testosterone levels, which is important for muscle mass, energy, and overall vitality.
Heart Health
- Cardiovascular Protection: Magnesium helps maintain a steady heart rhythm and supports overall cardiovascular health by regulating blood pressure and reducing the risk of heart disease.
Bone Health
- Bone Strength: Magnesium is essential for maintaining strong bones and preventing osteoporosis, especially as men age.
Exercise Performance
- Enhanced Performance and Recovery: Magnesium aids in muscle function and energy production, improving exercise performance and speeding up recovery after workouts.
Mental Health
- Mood and Stress Reduction: Magnesium helps regulate neurotransmitters that influence mood, reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Metabolic Health
- Blood Sugar Control: Magnesium helps regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Metabolic Function: It supports various metabolic processes, including energy production and protein synthesis.
Sleep Quality
- Improved Sleep: Magnesium promotes relaxation and helps regulate sleep patterns, leading to better sleep quality.
Migraine Prevention
- Reduced Migraine Frequency: Regular magnesium intake can help reduce the frequency and severity of migraines.
Including magnesium-rich foods in your diet or considering supplements can help you reap these benefits.
Magnesium supplements
Magnesium supplements come in various forms, each with its own benefits. Here are some popular types and their specific advantages:
Types of Magnesium Supplements
- Magnesium Citrate
- Benefits: Highly absorbable and often used to improve digestion and relieve constipation.
- Magnesium Glycinate
- Benefits: Known for its calming effects and is often recommended for improving sleep and reducing anxiety.
- Magnesium Oxide
- Benefits: Contains a high amount of elemental magnesium but is less easily absorbed. Often used for treating migraines and constipation.
- Magnesium Chloride
- Benefits: Easily absorbed and can be used to treat magnesium deficiency.
- Magnesium Malate
- Benefits: Known for its energy-boosting properties and is often recommended for chronic fatigue syndrome.
- Magnesium Taurate
- Benefits: Supports heart health and is beneficial for cardiovascular function.
- Magnesium L-Threonate
- Benefits: Known for its potential to improve cognitive function and brain health.
Popular Brands
- Nature Made Extra Strength Magnesium Oxide: Known for its high potency.
- Legion Sucrosomial Magnesium: Supports athletic performance.
- BioEmblem Triple Magnesium Complex: Offers a blend of different types of magnesium for comprehensive benefits.
- KAL Magnesium Glycinate: Best for relaxation and sleep.
Dosage and Considerations
The appropriate dosage can vary based on individual needs and health conditions. Consulting with a healthcare professional is always a good idea to determine the right dosage for you.
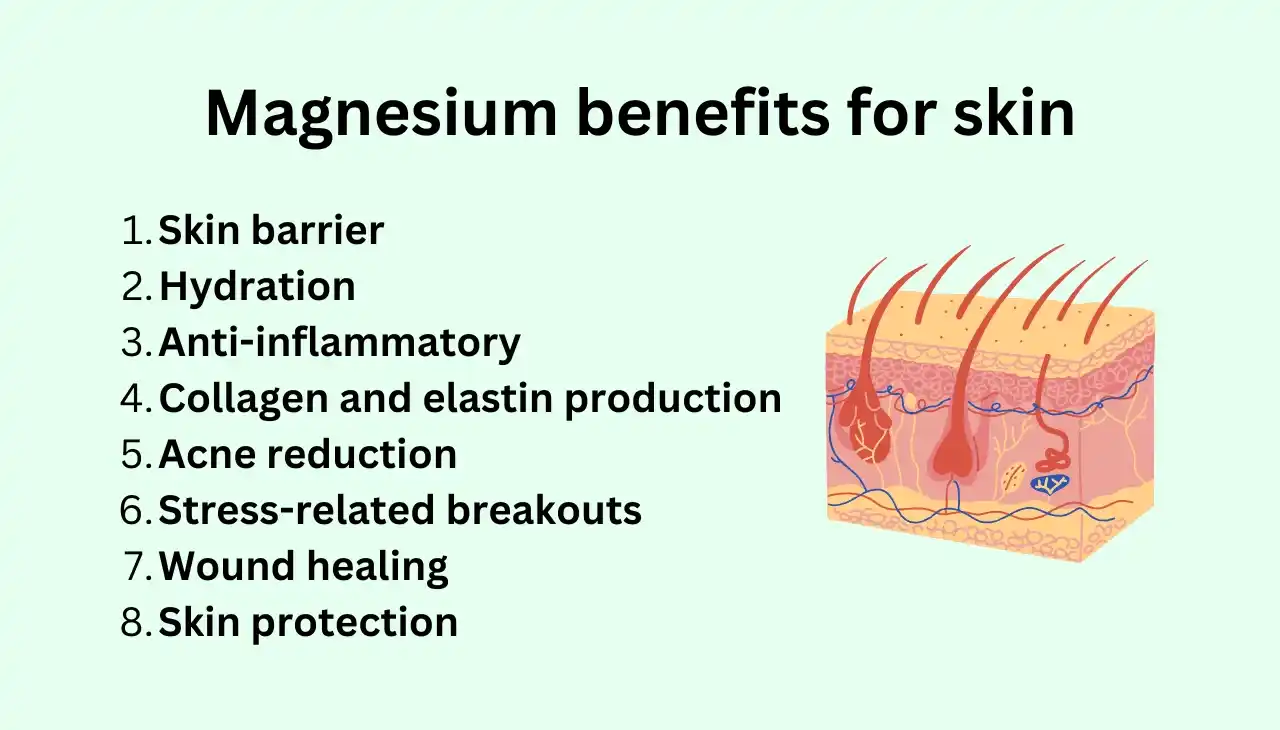
Magnesium benefits for skin
Magnesium offers several benefits for skin health, both when taken internally and applied topically. Here are some key advantages:
Hydration and Moisture
- Improves Skin Hydration: Magnesium helps maintain healthy levels of fatty acids in the skin, which are essential for keeping it moisturized and preventing dryness.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
- Reduces Inflammation: Magnesium can help soothe irritated skin and reduce redness and inflammation, making it beneficial for conditions like acne and eczema.
Stress Reduction
- Lowers Cortisol Levels: By reducing cortisol, the stress hormone, magnesium can help prevent stress-related skin issues such as acne breakouts.
Cellular Repair and Regeneration
- Promotes Skin Repair: Magnesium aids in cellular repair and regeneration, helping to heal damaged skin and promote the growth of new skin cells.
Anti-Aging Effects
- Reduces Wrinkles and Fine Lines: By supporting the production of collagen, magnesium can help maintain skin elasticity and reduce the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
Hyperpigmentation and Sun Damage
- Reduces Hyperpigmentation: Magnesium can help lighten dark spots and reduce the effects of sun damage on the skin.
Topical Application
- Magnesium Lotions and Oils: Applying magnesium-rich lotions or oils can directly benefit the skin by moisturizing and soothing it.
Including magnesium in your diet through foods or supplements, as well as using topical magnesium products, can help you achieve healthier, more radiant skin.
Magnesium supplements side effects
While magnesium supplements can offer numerous health benefits, they can also cause side effects, especially if taken in high doses.
Common Side Effects
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramping are common side effects, particularly with high doses.
- Digestive Discomfort: Some forms of magnesium, like magnesium oxide, are more likely to cause digestive discomfort.
Serious Side Effects
- Low Blood Pressure: Extremely high intakes can lead to hypotension (low blood pressure).
- Irregular Heartbeat: Very high doses can cause an irregular heartbeat and, in severe cases, cardiac arrest.
- Kidney Problems: Excessive magnesium can lead to kidney issues, especially in individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions.
- Central Nervous System Effects: High levels can cause symptoms like lethargy, confusion, and even loss of central nervous system control.
Other Potential Issues
- Muscle Weakness: Overconsumption can lead to muscle weakness and fatigue.
- Facial Flushing: Some people may experience facial flushing as a reaction to high magnesium levels.
Precautions
- Consult a Healthcare Professional: It’s always best to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
- Start with Lower Doses: If you’re new to magnesium supplements, starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it can help minimize side effects.
Benefits of Magnesium
- Magnesium: Your Heart’s Best Friend
- Magnesium regulates heartbeat and maintains healthy blood pressure levels.
- It acts as a conductor of the heart’s orchestra, ensuring perfect harmony.
- Maintaining adequate magnesium levels can reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- A study found that people with higher magnesium intake had a 30% lower risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Magnesium: Mood Booster
- Calming the Storm: Magnesium helps regulate neurotransmitters, reducing the whirlwind of worries in the mind.
- Lifting the Fog: Studies link low magnesium levels to an increased risk of depression.
- Magnesium supplementation is as effective as an antidepressant drug in treating mild to moderate depression.
- Magnesium’s Role in Sleep and Sleep Quality
- Magnesium regulates the production of melatonin, a hormone controlling sleep-wake cycles.
- It activates GABA receptors in the brain, a neurotransmitter that calms the nervous system, aiding relaxation and sleep.
- A study in the Journal of Research in Medical Sciences found magnesium supplementation improved sleep quality in elderly patients with insomnia.
- Magnesium may be beneficial for those struggling with nighttime jitters.
- Magnesium: A Metabolic Maestro
- Magnesium aids in blood sugar control, balancing sugary treats and processed foods.
- Crucial for insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, unlocking cells for glucose entry and energy use.
- Insufficient magnesium can lead to type 2 diabetes.
- A meta-analysis found a 15% decrease in type 2 diabetes risk with every 100 mg increase in magnesium intake.
- Magnesium’s Role in Bone Health
- Magnesium regulates calcium levels and activates vitamin D, crucial for bone health.
- It acts as a construction site, ensuring effective calcium use for strong bones.
- Research in Nutrients indicates higher magnesium intake correlates with higher bone mineral density in both genders.
- Magnesium is essential for maintaining a healthy skeleton.

- Magnesium: A Woman’s Best Friend During PMS Relief
- Magnesium aids in regulating cortisol levels and supports progesterone production, aiding in PMS relief.
- A study in the Journal of Women’s Health found magnesium supplementation significantly reduced PMS symptoms.
- Magnesium is recommended for women during the dreaded time of the month.
- Magnesium Sources
- Green Goodness: Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are natural magnesium sources.
- Nuts and Seeds: Get your daily dose of magnesium from delicious almonds, cashews, pumpkin seeds, and sunflower seeds.
- Whole Grains: Quinoa, brown rice, and oatmeal are rich in magnesium.
- Beans and Legumes: Black beans, kidney beans, and chickpeas are excellent magnesium sources.
- Hummus: These legumes can be added to soups, salads, or hummus for a magnesium-rich treat.
- Choosing the Right Magnesium Supplement
- Magnesium Glycinate: Gentle Giant
- Highly absorbable and easy on the stomach.
- Bound to amino acid glycine for absorption and brain calming.
- Magnesium Citrate: Digestive Aid
- Highly absorbable and mild laxative.
- Budget-Friendly option
- More concentrated and requires smaller doses for the same amount of elemental magnesium.
- Tablets vs. Pills vs. Capsules: Personal preference
- Tablets are cost-effective, capsules easier to swallow, and pills a good middle ground.
- Choose a form that you’ll consistently take.
- Magnesium Safety and Side Effects
- Overdoing magnesium can lead to diarrhea, requiring reduction or smaller doses.
- Cautious individuals with kidney problems, heart block, or certain medications should consult a healthcare provider before starting magnesium supplementation.
- Recommended daily allowance for men: 400-420mg, women: 310-320 mg.
- Individual needs vary based on age, activity level, and overall health. Start with a lower dose and gradually increase until the desired amount is reached.
Conclusion
Magnesium, a miraculous mineral, offers wide-ranging benefits to the body, including supporting heart health, mental well-being, better sleep, and stronger bones. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the body’s optimal functioning. Prioritizing magnesium-rich foods in your diet and considering supplementation can help tap into its power, leading to significant improvements in overall health and well-being.
FAQ
Can I get enough magnesium from my diet alone, or do I need supplements?
It's definitely possible to get enough magnesium from your diet alone, but it requires conscious effort. A varied diet rich in leafy greens, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and legumes can provide adequate magnesium. However, factors like soil depletion, processed foods, and certain medical conditions can make it challenging to meet your needs through diet alone. If you're concerned about your magnesium intake, consult with a healthcare provider. They can test your magnesium levels and recommend supplements if necessary.
Is it possible to overdose on magnesium?
While it's rare to overdose on magnesium from food sources, it is possible to take too much in supplement form. The upper limit for supplemental magnesium is typically around 350-400 mg per day for adults. Excessive magnesium intake can lead to symptoms like diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramping. In severe cases, it can cause irregular heartbeat and cardiac arrest. However, these extreme cases are usually only seen in people with kidney problems who can't properly excrete excess magnesium. Always follow the suggested doses and contact with your doctor before beginning any new supplement program.
How long does it take to see the benefits of increasing magnesium intake?
The timeline for experiencing benefits from increased magnesium intake can vary depending on your initial magnesium levels and the specific symptoms you're addressing. Some people report improved sleep and reduced muscle tension within a few days of starting magnesium supplementation. For other effects, like improvements in bone density or significant changes in mood, it may take several weeks to a few months of consistent adequate intake. Remember, everybody is different, so your experience may vary. Consistency is key when it comes to seeing the long-term benefits of magnesium.
Can magnesium interact with medications I'm taking?
Yes, magnesium might interact with different kinds of medications. For example, it can interfere with the absorption of certain antibiotics and osteoporosis medications. It may also enhance the effects of some blood pressure medications. If you're taking any prescription medications, especially for heart conditions, diabetes, or osteoporosis, it's crucial to consult with your healthcare provider before starting magnesium supplements. They can advise you on potential interactions and help you determine the right dosage and timing for your supplements.
I've heard that magnesium can help with migraines. Is this true?
Yes, there is evidence to suggest that magnesium can help prevent and reduce the severity of migraines in some people. Magnesium plays a role in neurotransmitter function and blood vessel regulation, both of which are involved in migraine pathology. Some studies have shown that people who suffer from migraines often have lower levels of magnesium compared to those who don't. The American Migraine Foundation even lists magnesium as a "probably effective" nutritional supplement for migraine prevention. However, as with any health condition, it's important to discuss with your healthcare provider before using magnesium as a treatment for migraines, as they can help determine if it's suited for your individual circumstance and walk you through the optimum dose.