Introduction
Have you ever noticed that your knees touch when your ankles don’t? This condition, known as knock knees or genu valgum, is more common than you might think. It’s especially prevalent in children, but it can also persist into adulthood. While it might seem like just a cosmetic issue, untreated knock knees can lead to serious health problems down the line. So, what exactly causes knock knees, and how to fix knock knees? Let’s dive in and explore the various treatment options available, both surgical and non-surgical.

How to repair knock knees in adults without surgery.
Fixing knock knees (genu valgum) in adults without surgery involves a combination of exercises, stretches, and lifestyle changes. Here are some effective methods:
Exercises and Stretches
- Hip Strengthening Exercises:
- Clamshells: Lie on your side with knees bent. Keep your feet together and elevate your upper knee, keeping your feet in touch.
- Side-Lying Leg Lifts: Lie on your side and lift your top leg upwards, keeping it straight.
- Side Steps with Resistance Band: Place a resistance band around your thighs and take side steps to strengthen your hip abductors.
- Inner Thigh Stretches:
- Butterfly Stretch: Sit with legs together and knees bent out to the sides. Gently push your knees down to the ground.
- Frog Stretch: Kneel on all fours and spread your knees apart while keeping your feet together.
- Balance and Stability Exercises:
- Single-Leg Stands: Stand on one leg for as long as possible, then switch legs.
- Heel Raises: Stand on your toes and slowly lower your heels back down.
Lifestyle Changes
- Footwear: Wear supportive shoes to help align your knees and hips properly.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on your knees.
- Diet: To promote bone health, consume a well-balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D.
Additional Tips
- Consistency: Perform these exercises regularly, ideally daily, to see improvement.
- Consult a Professional: It’s always a good idea to consult with a physiotherapist for personalized advice and to ensure you’re doing the exercises correctly.
These methods can help improve the alignment of your knees and reduce discomfort over time. If you have any underlying conditions or severe symptoms, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional.
Knock knees exercises
Here are some effective exercises to help correct knock knees (genu valgum):
- Clamshells
- How to do it: Get lie on your side with your knees bent. Keep your feet together and elevate your upper knee, keeping your feet in touch.
- Benefits: Strengthens the hip abductors and external rotators.
- Side-Lying Leg Lifts
- How to do it: Lie on your side and lift your top leg upwards, keeping it straight.
- Benefits: Strengthens the hip abductors.
- Butterfly Stretch
- How to do it: Sit with your feet together and knees bent out to the sides. Gently push your knees down to the floor.
- Benefits: Stretches the inner thighs and improves hip flexibility.
- Crab Walk with Resistance Band
- How to do it: Place a resistance band around your thighs and take side steps.
- Benefits: Strengthens the hip abductors and improves knee alignment.
- Single-Leg Stands
- How to do it: Stand on one leg for as long as possible, then switch legs.
- Benefits: Improves balance and stability.
- Heel Raises
- How to do it: Stand on your toes and slowly lower your heels back down.
- Benefits: Strengthens the calves and improves ankle stability.
- Seated Internal Rotation Stretch
- How to do it: Sit on the floor with your legs extended. Bend one knee and rest the foot on the opposing thigh. Gently press the knee down.
- Benefits: Stretches the hip internal rotators.
- Resistance Band Squats
- How to do it: Place a resistance band around your thighs and perform squats.
- Benefits: Strengthens the quadriceps and glutes, and helps prevent the knees from collapsing inward.
- Full Plank
- How to do it: Hold a plank position with your body straight from head to heels.
- Benefits: Strengthens the core and stabilizes the hips and knees.
- Frog Stretch
- How to do it: Kneel on all fours and spread your knees apart while keeping your feet together.
- Benefits: Stretches the inner thighs and improves hip flexibility.
These exercises can help improve the alignment of your knees and reduce discomfort over time. Consistency is crucial, so work them into your everyday routine. If you have any underlying conditions or severe symptoms, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional.
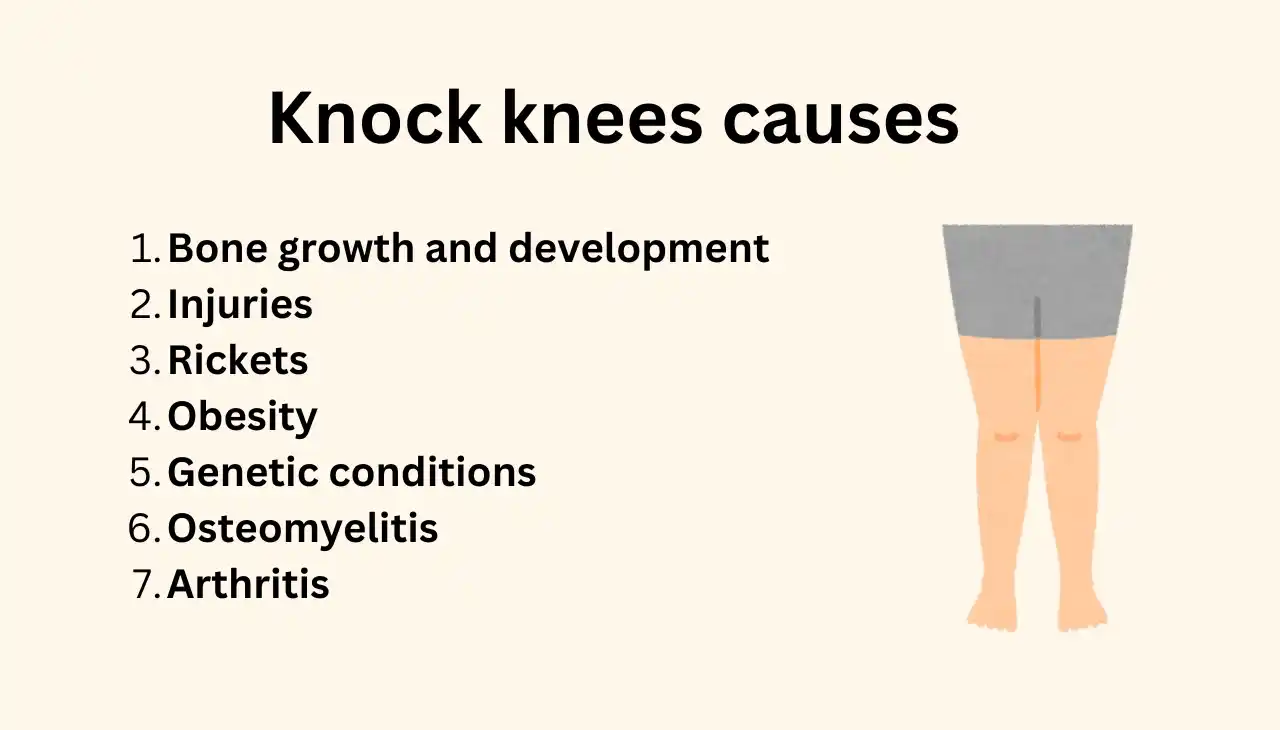
How to check knock knees
To check for knock knees (genu valgum), you can follow these steps:
Self-Assessment
- Stand Straight: Stand on a flat surface with your feet together, forming a “V” shape.
- Observe Your Knees: Look at your knees. If they touch each other while your ankles remain apart, you may have knock knees.
- Measure the Gap: Measure the distance between your ankles. A significant gap (more than a few centimeters) while your knees are touching indicates knock knees.
Professional Assessment
- Physical Examination: A healthcare professional will observe your leg alignment while you stand upright.
- X-Ray: The most accurate way to diagnose knock knees is through a standing X-ray. A straight line is drawn between the hip and the ankle. If this line passes outside the knee, it confirms the presence of genu valgum.
Additional Tips
- Consult a Specialist: If you suspect you have knock knees, it’s best to consult with an orthopedic specialist for a thorough evaluation and personalized advice.
- Monitor Symptoms: Pay attention to any pain or discomfort in your knees, hips, or lower back, as these can be associated with knock knees.
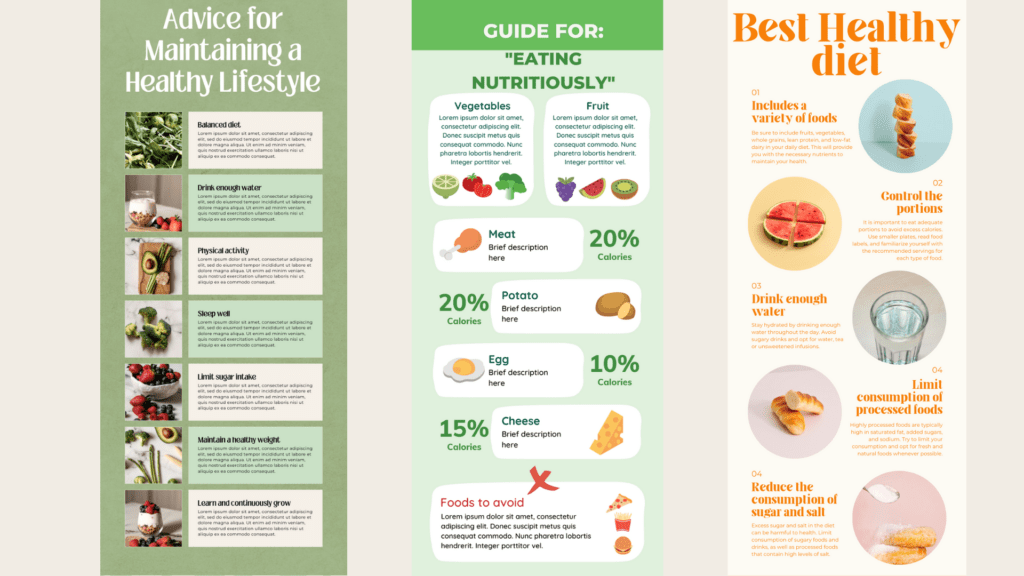
Knock knees causes
Knock knees (genu valgum) can be caused by various factors, including:
Common Causes
- Developmental: It’s normal for children to go through a phase of knock knees between the ages of 2 and 6. As they mature, this issue typically resolves itself.
- Genetics: Knock knees may be more likely for some people due to their genetic makeup.
- Injury or Trauma: Damage to the knee or leg bones can lead to knock knees.
- Infections: Bone infections like osteomyelitis can affect knee alignment.
- Arthritis: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis can cause knock knees due to joint damage.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of vitamin D and calcium can lead to rickets, which affects bone development and can cause knock knees.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts additional pressure on the knees, potentially leading to knock knees.
- Metabolic Diseases: Conditions like renal (kidney) failure can affect bone health and alignment.
Less Common Causes
- Congenital Conditions: Some people are born with conditions that affect bone development.
- Bone Tumors: Benign bone tumors can alter the alignment of the knees.
If you suspect you have knock knees, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized advice.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options for Knock Knees
- Exercises for Strengthening and Flexibility: Targeted exercises like Figure 4 Stretch and Butterfly Stretch can improve knee alignment and strengthen muscles around the knee.
- Clamshells and Lying Leg Lifts: These exercises focus on the glutes and outer thighs, which play a significant role in stabilizing the knees.
- Squats for Knock Knees: Squats strengthen the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes, supporting proper knee alignment.
- Physiotherapy and Professional Guidance: Physiotherapists can create personalized exercise programs and teach proper techniques to avoid injury.
- Lifestyle Changes to Support Knee Health: Diet for Bone Health: Include leafy greens, dairy products, and fatty fish in your diet.
- Weight Management for Knee Health: Weight loss can reduce knee strain, improving alignment and reducing pain.
- Footwear Choices and Orthotic Support: Choose shoes with good arch support and stability.
- Orthotic Shoes and Braces: Custom orthotics or braces may be necessary to correct gait issues associated with knock knees.
Surgical Options for Knock Knees
- Non-surgical treatments may not always be sufficient for severe symptoms or ineffective non-surgical methods.
- Surgery is recommended when knock knees cause significant pain, mobility issues, or affect quality of life.
- Common surgical procedures include knee replacement surgery for older adults with severe arthritis, and osteotomy procedure for younger patients.
- Post-surgery recovery and rehabilitation are crucial for regaining full function.
- Recovery times can vary, but most patients expect several months.
- Rehabilitation exercises are vital after surgery to rebuild muscle strength and improve knee alignment.
How to fix knock knees in kids
Fixing knock knees (genu valgum) in kids often involves non-surgical methods, as many children naturally outgrow this condition. Here are some effective approaches:
- Exercises and Stretches
- Clamshells: Lie on the side with knees bent. Keep feet together and lift the top knee while keeping feet in contact. This strengthens the hip abductors.
- Butterfly Stretch: Sit with feet together and knees bent out to the sides. Gently press knees down towards the floor to stretch the inner thighs.
- Side-Lying Leg Lifts: Lie on the side and lift the top leg upwards, keeping it straight. This strengthens the hip abductors.
- Heel Raises: Stand on toes and slowly lower heels back down. This strengthens the calves and improves ankle stability.
- Bracing
- Night Braces: In some cases, a night brace can help guide the bones to grow in the correct position.
- Footwear
- Supportive Shoes: Wearing supportive shoes can help align the knees and hips properly.
- Weight Management
- Healthy Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on the knees.
- Monitoring and Professional Guidance
- Regular Check-ups: Regular visits to a pediatrician or orthopedic specialist can help monitor the condition and provide personalized advice.
When to Seek Further Help
- If knock knees persist beyond age 7 or worsen, it may be necessary to consult a specialist for further evaluation and potential treatment options.
These methods can help improve knee alignment and reduce discomfort over time. If you have any specific concerns or need more detailed guidance, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional.
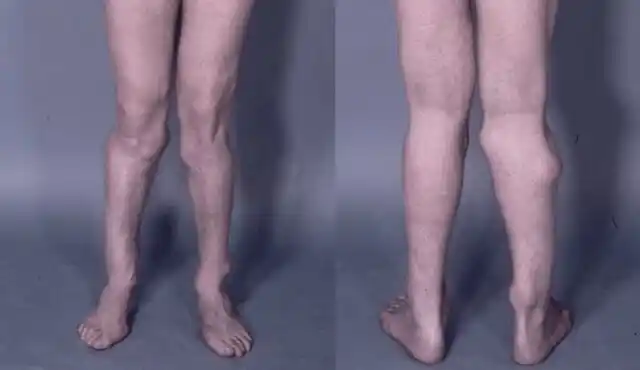
Are knock knees bad
Knock knees (genu valgum) are not necessarily “bad,” but they can cause certain issues depending on their severity and the underlying cause. Here are some points to consider:
Potential Issues
- Joint Pain: Severe knock knees can lead to discomfort or pain in the knees, hips, or ankles due to misalignment.
- Gait Problems: It can affect the way you walk, potentially leading to further joint issues over time.
- Increased Wear and Tear: Misalignment can cause uneven wear on the knee joint, increasing the risk of arthritis later in life.
- Physical Activity Limitations: In some cases, knock knees can limit participation in certain physical activities or sports.
When It’s Not a Major Concern
- Children: For most children, knock knees are a normal part of development and usually correct themselves by age 7 or 8.
- Mild Cases: Mild knock knees that do not cause pain or functional limitations are often not a cause for concern.
Management and Treatment
- Exercises: Strengthening and stretching exercises can help improve alignment and reduce discomfort.
- Supportive Footwear: Wearing supportive shoes can help align the knees and hips properly.
- Weight Management: Keeping your weight in check helps ease the strain on your knees.
- Professional Guidance: Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide personalized advice and treatment options.
If you or someone you know has knock knees and is experiencing pain or functional limitations, it’s a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
Conclusion
In summary, knock knees are more than just a cosmetic concern—they can lead to serious health issues if left untreated. Whether you’re exploring non-surgical options like exercises and physiotherapy or considering surgery, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action. Remember, consistency is key. By following a structured treatment plan and sticking with it, you can improve your knee alignment, reduce discomfort, and potentially correct knock knees over time.
Ultimately, the journey to fixing knock knees involves a combination of exercises, lifestyle changes, and possibly surgical intervention. Whatever path you choose, taking proactive steps to address the condition is the best way to ensure a healthy and active future.
FAQ:
Can knock knees correct themselves without treatment?
In children, knock knees often correct themselves naturally as they grow, particularly between the ages of 3 and 7. However, if the condition persists into adolescence or adulthood, it's unlikely to resolve without intervention. In such cases, exercises, lifestyle changes, or even surgical options may be needed to correct the alignment and prevent further complications.
Are there any specific exercises that should be avoided if I have knock knees?
Yes, certain exercises that put excessive stress on the knees or encourage inward knee movement should be avoided. High-impact activities like running on hard surfaces, deep squats without proper form, and exercises that cause the knees to cave in (like certain lunges) can exacerbate the condition. It’s important to focus on exercises that strengthen the muscles supporting proper knee alignment, such as clamshells and leg lifts, and to consult with a physiotherapist for personalized guidance.
How long does it take to see improvement in knee alignment with non-surgical treatments?
The timeline for improvement can vary depending on the severity of the knock knees, the consistency of treatment, and individual factors like age and overall health. Generally, with regular exercise and physiotherapy, you may start to notice improvements in alignment and reduction in pain within a few months. However, significant correction and long-term results may take several months to a year of consistent treatment.
What dietary changes can support the correction of knock knees?
A diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and other bone-strengthening nutrients is crucial. This includes foods like dairy products, leafy greens, fatty fish, and fortified cereals. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet can reduce the strain on your knees, which is particularly important if obesity is contributing to the condition. It’s advisable to consult with a nutritionist or healthcare provider to create a diet plan that supports your specific needs.
When is it necessary to consider surgery for knock knees?
Surgery is typically considered when non-surgical treatments have not provided sufficient relief, and the condition is causing significant pain, mobility issues, or impacting quality of life. It may also be recommended if the knock knees are severe or worsening over time. The decision to undergo surgery should be made in consultation with an orthopedic specialist, who can assess the severity of the condition and discuss the best surgical options based on your individual circumstances.